MODULES
Collapse Of Water Column
Problem Definition:
This test case is also referred as the Dam break problem. The domain is a 5 × 1.5 rectangular tank with a 1 × 1 water column placed at the left corner. The fluids are water and air. The Reynolds number for the simulation is chosen to be 43000, while the Froude number is unity. The domain is discretised using hexahedral elements. The simulation is carried out using a constant time step of t = 0.001 until t=2.5. The schematic diagram is shown in Fig. 1.1. The values of dynamic viscosity (μ) are calculated from the following relation:
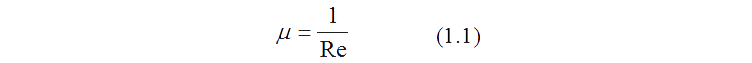
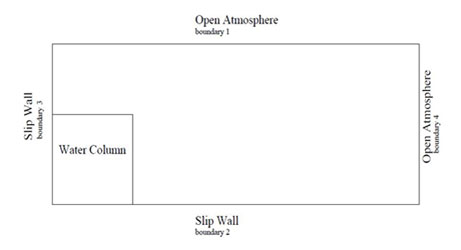
Figure 1.1: Collapse of Water Column
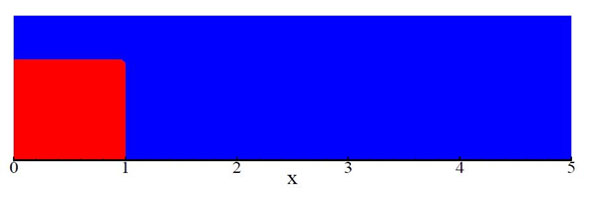
Figure 1.2: Initial position of water column
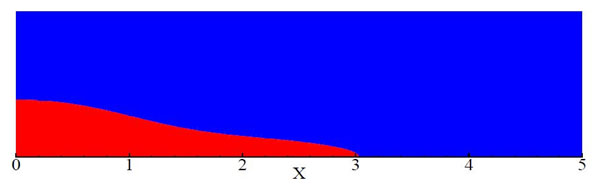
Figure 1.3: Position of water front after 2 seconds
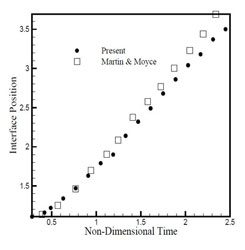
Figure 1.4: Comparison of dam front
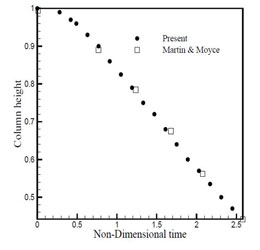
Figure 1.5: Comparison of dam height
[1] Martin J.C. and Moyce W. (1952) ‘An experimental study of collaspe of liquid column on the rigid horizontal plan’, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, vol. 244, pp. 312–324.


