DC Chair: Prof. M. K. Bhuyan
Short abstract:
The work
involved the detection and correction of regions affected by a phenomenon
called PURPLE HAZE seen in certain camera models. While the exact source of
the purple flare remained unknown,
the
problem of detecting the affected HAZE region, despite the presence of a
prominent background texture was quite interesting. The CORE of the work,
revolved around both the DETECTION and
COMPENSATION of the PURPLE HAZE distortion. The detection procedure involved
a heuristic CHROMATIC DISTANCE RATIO in the CB-CR domain revolving around
two referential PIVOTS. The correction
on the
other hand involved RESTORATION of the GREEN channel in places affected by
the HAZE (done as a COLOR PIXEL operation/manipulation/restoration).

JOURNALS:
1) P. Malik, and
K. Karthik, “Iterative content adaptable purple fringe detection”,
Signal, Image and Video Processing (SIViP), vol. 12, pp. 181–188 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1144-1. 2)
2) P. Malik and
K. Karthik, "Correction of complex purple fringing by green-channel
compensation and local luminance adaptation," in IET Image
Processing, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 154-167, 10/1/2020.
Selective
conferences:
1) K. Karthik
and P. Malik, "Purple fringing aberration detection based on content
adaptable thresholds", in proceedings of International Conference on
Smart System, Innovations and Computing (SSIC-2017), pages 63-71, Jaipur,
India, 2017. [Best Sessional Paper Award]
DC Chair: Prof. M. K. Bhuyan
Short abstract:
Owing the ubiquitous deployment of
face-recognition units at various points, "face-masquerading" is
certainly possible via synthetic facial-imitations of some target
individual. These "imitations" can be
executed either in a crude way with a planar
print/digital image or in a much more sophisticated manner via
"prosthetics".
Since the spoofing modality/type is hard to
predict, what is well understood is the INTRINSIC NATURAL FACE-SPACE.
Furthermore, counter-spoofing should operate at a layer where
subject-content must be ignored.
What should be learnt is the high-level
presentation form of the face or face-like object presented to the
still-camera. On this front, a CONTIGUOUS RANDOM SCAN based architecture
is proposed and deployed to build a content-agnostic/subject-independent
model for the NATURAL FACE CLASS ALONE. Works effectively against
planar-spoofing and even prosthetics despite depth variability (due to
the one-mask-fits-many, over-smoothing constraint).
The "contiguous random scan" is a technology
transfer from an application invented by Matias and Shamir (1987) which
involved application of SPACE FILLING CURVES for compressing encrypted
videos.
As second contribution, to attack
PRINT-SPOOF-presentations, a CONTRAST REDUCTIONISTIC IMAGE LIFE-TRAIL
based on ITERATIVE FUNCTIONAL MAPS is proposed, to segregate natural
contrast rich faces with SELF-SHADOWS from PRINT-SPOOF-presentations. NATURAL
face-images tend to have longer LIFE-trails as compared to
PRINT-SPOOF-images.

Two instances of
the RANDOM SCAN over the same patch and then different statistics are
generated.
The
process is content agnostic but the first order and second order pixel
intensity correlation statistics are preserved.
This can
be used to trap the NATURAL INTRINSIC ACQUISITION NOISE picked from NORMAL
FACE PRESENTATIONS.

Natural facial
presentations are contrast rich and have prominent self-shadows. These can
be discriminated from planar low-contrast spoof-presentations by passing the
test image through an ITERATIVE-FUNCTION-SYSTEM such as a
LOGISTIC MAP
which gradually dissolves the content and converts the parent image to a
zero contrast image. This IMAGE SEQUENCE is called a LIFE-TRAIL and
natural faces exhibit longer life-trails as compared to their spoofed
counter-parts. The LOGISTIC MAP used here is,

JOURNALS:
1) Balaji R.
Katika, K. Karthik, Face anti-spoofing by identity masking using random
walk patterns and outlier detection. Pattern Anal Applic 23, 1735–1754
(2020).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-020-00875-8
2) Balaji R.
Katika, K. Karthik, Image life trails based on contrast reduction models
for face counter-spoofing. EURASIP J. on Info. Security 2023, 1 (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13635-022-00135-8
Selective
Conferences:
1) K. Karthik and
K. Balaji,
"Identity
Independent Face Anti-spoofing based on Random Scan Patterns",
In Proceedings of 8th International conference on Pattern Recognition and
Machine Intelligence (PREMI 2019),
Tezpur, Assam, India, December 17-20, 2019.
2)
K. Karthik and
K. Balaji Rao,"Image
Quality Assessment based Outlier detection for Face Anti-Spoofing",
in proceedings of International Conference on Communication Systems,
Computing and IT Applications (CSCITA 2017), Mumbai, India, April 7-8, 2017.
3)
K. Karthik, K.
Balaji Rao, "Face
Anti-spoofing Based on Sharpness Profiles", in
proceedings of International Conference on Industrial and Information
Systems (ICIIS 2017), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, December 15-16, 2017.
3)
Shoubhik Chakraborty (May 18th, 2023)
Graph based Classification Techniques for Pig Breed
Identification based on Handcrafted Visual Descriptors
External/Indian Examiner: Prof.
Balasubramanian Raman (CSE/IIT Rourkee)
DC Chair: Prof. M. K. Bhuyan
Short abstract:
Limited, noisy, heterogeneous visual data
stemming from MUZZLE images taken from Pigs belonging to
different breeds pose many challenges, not just from the point
of view of identifying and isolating those features and
statistics which are discriminatory in nature, but also from the
point of view of constructing a suitable breed-centric model
(aided by an inferencing mechanism), which is robust and
stable.
The work in this light has three primary
contributions:
-
Designing and selecting a set of Handcrafted Colour and
Texture based visual descriptors which are
breed-discriminatory.
- Devising
a feature-specific siphoning policy and model for
segregating breeds serially.
- Using
Spanning Trees in DUAL MODE (MIN-tree and MAX-tree forms)
for binding breed-specific features and devising a
NOVEL test-point INDUCTION procedure for producing an
OUTLIER score, whether the point is in the INTERIOR or
EXTERIOR of the breed-cluster.
Given the diversity of data on hand
and the limited training set available to build the model,
CROSS-testing results were very promising: DUROC-breed
(93.85%), GHUNGROO (97.48%), HAMPSHIRE (94.27%) and
YORKSHIRE (100%).


Texture descriptor/filter in the form of the
GRADIENT SIGNIFICANCE MAP (GSM)
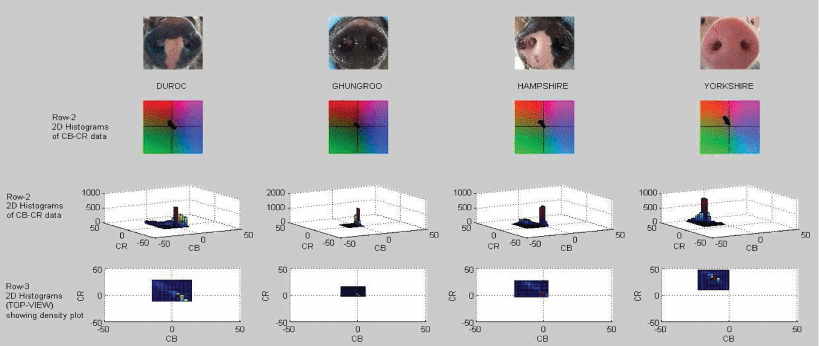
BASELINE Color descriptors from the CB-CR palette.

A feature driven, hierarchical breed siphoning
policy (as a tree) generated using a CLUSTER DISTANCE TABLE.
UNPUBLISHED WORK involving a
data-driven approach in which TREES are constructed over the
feature vectors.

MAX-tree for detecting OUTLIERS near the cluster
but outside the convex-hull.

MIN-tree for detecting OUTLIERS at
the periphery of the cluster but within the convex-hull.









