Research
NLP for Indian Languages
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has emerged as a groundbreaking field, venturing into the rich tapestry of Indian languages, unlocking a mosaic of linguistic diversity. With India’s linguistic landscape boasting over 22 officially recognized languages and a multitude of dialects, NLP endeavors to bridge the gap by decoding, understanding, and generating content in Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, and more. From sentiment analysis to machine translation and speech recognition, NLP pioneers strive to preserve and celebrate India’s linguistic heritage while propelling technology to resonate with the hearts and minds of millions, fostering inclusivity and accessibility across linguistic boundaries.
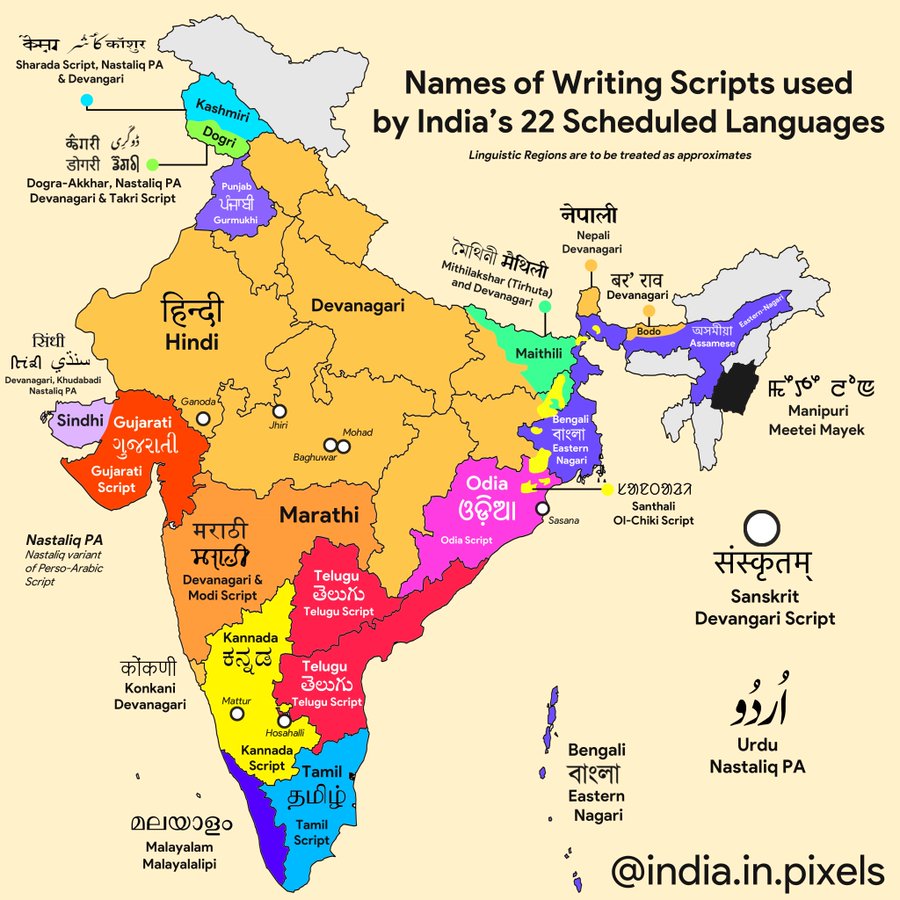
Langauge diversity in India
IndiSocialFT: Multilingual Word Representation for Indian languages in code-mixed environment
The increasing number of Indian language users on the internet necessitates the development of Indian language technologies. In response to this demand, our paper presents a generalized representation vector for diverse text characteristics, including native scripts, transliterated text, multilingual, code-mixed, and social media-related attributes. We gather text from both social media and well-formed sources and utilize the FastText model to create the "IndiSocialFT" embedding. Through intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation methods, we compare IndiSocialFT with three popular pre-trained embeddings trained over Indian languages. Our findings show that the proposed embedding surpasses the baselines in most cases and languages, demonstrating its suitability for various NLP applications.
IndiSentiment140: Sentiment Analysis Dataset for Indian Languages with Emphasis on Low-Resource Languages using Machine Translation
Sentiment analysis(SA), a fundamental aspect of Natural Language Processing (NLP), involves classifying emotions, opinions, and attitudes in text data. In the context of India, with its vast linguistic diversity and low-resource languages, the challenge is to support SA in numerous Indian languages. This study explores the use of machine translation to bridge this gap. The investigation examines the feasibility of machine translation for creating SA datasets in 22 Indian languages. Google Translate, with its extensive language support, is employed for this purpose in translating the Sentiment140 dataset. The study aims to provide insights into the practicality of using machine translation in the context of India's linguistic diversity for SA datasets. Our findings indicate that a dataset generated using Google Translate has the potential to serve as a foundational framework for tackling the low-resource challenges commonly encountered in sentiment analysis for Indian languages.