Prof. Chandan Das
Professor
Key Research Areas :Wastewater Treatment, Bioremediation, Membrane based Separation Process.
- Phone No: +91 361 258 2268
- Email: cdas@iitg.ac.in
- Room No: 0206
Research
Membrane Separation Technology
Treatment of industrial oily wastewater for onshore oil production supplied by Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) Eastern region, Nazira, Assam, India is done by cross flow filtration cell. Membrane performance and permeate quality are compared at laminar and turbulent flow regime with variation of transmembrane pressure drops. Different diffusion models are assumed to predict the theoretical flux and compared with experimental flux values.
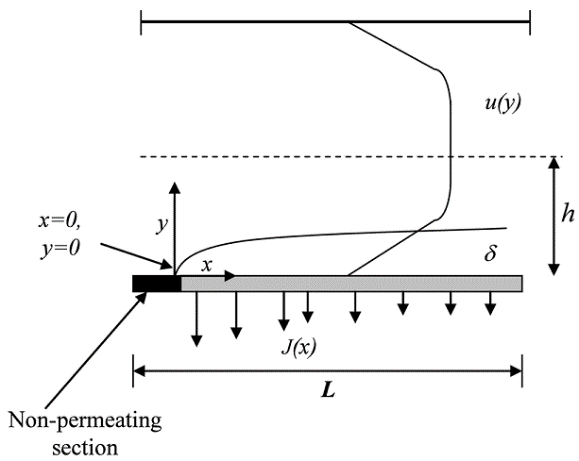
Figure: Schematic for concentration polarization over the membrane surface.
A membrane based technology for recovery of organic solvent from coal-solvent mixture is developed. Recovered organic solvent is again reused for improvement of coal properties in subsequent extraction stages. A low cost ceramic membrane is developed from steel industry waste iron ore slime (IOS) and is applied to recover organic solvent from coal-solvent mixture. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis of both coals (A and B), permeate and organic solvent are done separately to verify the absence of coal particle in permeate sample.
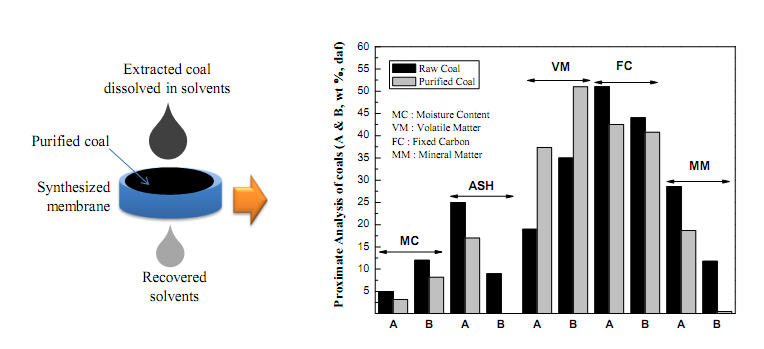
Figure: Recovery of organic solvent used in coke production
Fruit juice clarification through membrane is also explored. Before juice clarification, pretreatment is necessary. Different pretreatment methods are applied for clarification of juice and physicochemical properties are compared.
A. Preparation, Functionalization, and Characterization of Electro-spun and Phase-inverted Cellulose acetate Membranes for Advanced Wastewater Treatment Applications
- Firstly, an empirical investigation into the impacts of time duration, voltage supply, concentration, and flow rate on the membrane average fiber diameter and surface pore size distribution was done using response surface methodology (RSM) based on central compact design (CCD) are presented. In addition, the effect of glutaraldehyde on membrane crosslinking was also assessed for further studies.
- Secondly, hybrid membranes from cellulose acetate (CA) and titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) were fabricated using a novel electro-spinning technique and evaluated as an adsorbent for the elimination of lead and copper metal ions. The impact of TiO2 NPs contents on the electro-spun membranes matrix was studied in detail. The impacts of various adsorption parameters, namely, pH, the amount of TiO2 nanoparticles, contact time, temperature, and kinetics of metal uptake were investigated using batch adsorption experiments. The model isotherms, such as Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R), Freundlich, and Langmuir were used to analyze the adsorption equilibrium data. Both pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order were preferred for kinetic model study.
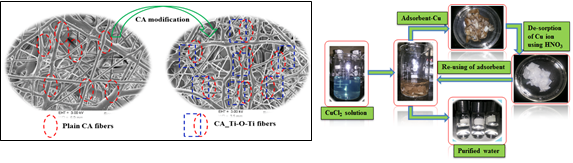
Figure: Electrospun nanofiber membranes
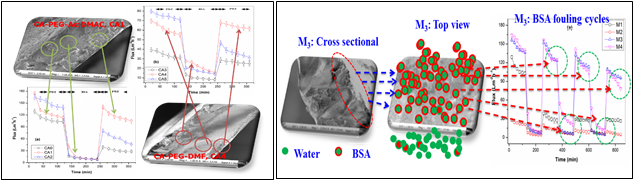
Figure: Phase inverted membrane for BSA removal
- Preparation and characterization of PP-PVA-PEG composite films for antimicrobial packaging applications
- For wide range of properties polymers are very commercially used in different industries for various applications. Our research work includes preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) products via different techniques like, casting, immersion precipitation and electro spinning and to make sustainable films for packaging and biomedical application. PVA is water soluble, nontoxic, non-carcinogenic, biodegradable, offers quite good mechanical strength, thermal resistance and compatible with different other natural polymer to prepare blend. But due to high aqueous solubility it have high tendency to absorb moisture. Also PVA film provides very low gas permeability. These restrict its use in packaging application. But it can act as plasticizer and can be used for blending with other polymer or used as modifier film on other polymer film, to provide better gas permeability. Polypropylene (PP) is most frequently used plastic films for packaging and storage system. For food packaging film should provide good gas permeability, antioxidant property thus antimicrobial property and good thermal and mechanical resistance. PP will provide better stability and PVA can be cross-linked with harmless natural crosslinking agent; like, citric acid, poly ethylene glycol (PEG). This will reduce the moisture absorbance property of the film and increase the anti-microbial property.
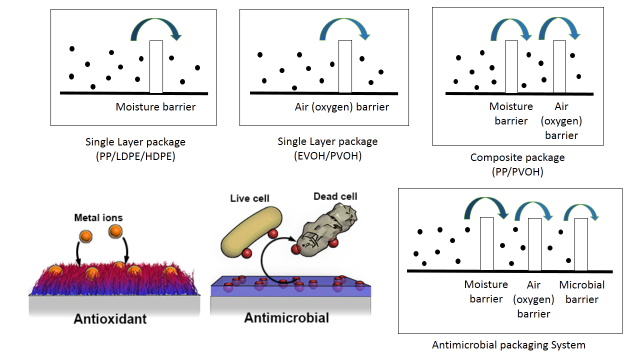
Figure: Anti microbial packaging
For wound dressing application material should have elastic, non-antigenic and biocompatible/biodegradable property, good surface absorbance for wound fluids, ability to protect the wound protected from any side contamination. PVA is able to simulate natural tissues and easily to be accepted in the body implantation. But due to water solubility, in contact to the wound PVA film can be damaged under stress or stretching which results in sticking to the wound surface. It can be avoided by crosslinking, but suitable harmless natural crosslinking agent and its effect can be studied as a possible framework for these applications.
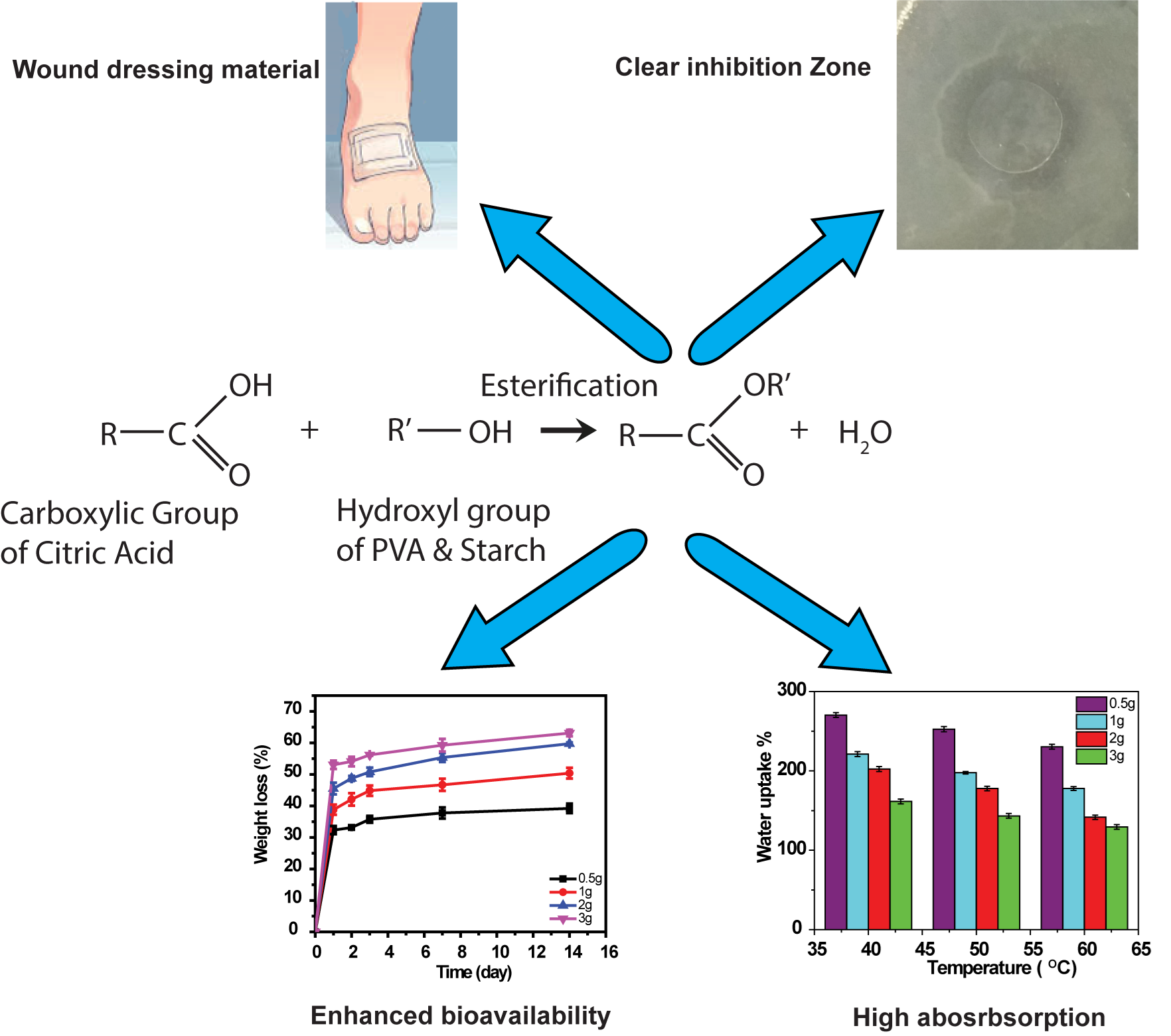
Figure: Wound dressing application
Water is the treasurable resource in the environment. Recycling of water from industrial effluents can offer substantial benefits towards living society. Thus, the treatment of wastewater is very significant activity towards water conservation and sustainability, rather than discharging untreated water to the surface water, rivers or oceans. Employment of advanced separation like spinning basket membrane module (SBMM) ultrafiltration for the treatment of industrial effluents and thereby production of recycled water for the water conservation and sustainability is a practical possibility in the recent. However, solid waste management is also a global issue that particularly brings developing countries into the attention due to the lack of appropriate strategies for the treatment, necessary resources and infrastructures etc. Recovery of valuable products using extraction process is an effective and innovative activity during waste management. In this direction, we are studying on the treatment of tea factory solid waste materials towards total polyphenols extraction as polyphenols have significant benefits on human health. The products which can be extracted from tea solid waste using solvent extraction methods are mainly polyphenols, caffeine, pigments, foaming reagents. Recovery of total polyphenols from the tea factory generated solid waste is novel and effective process to maintain green management of solid waste.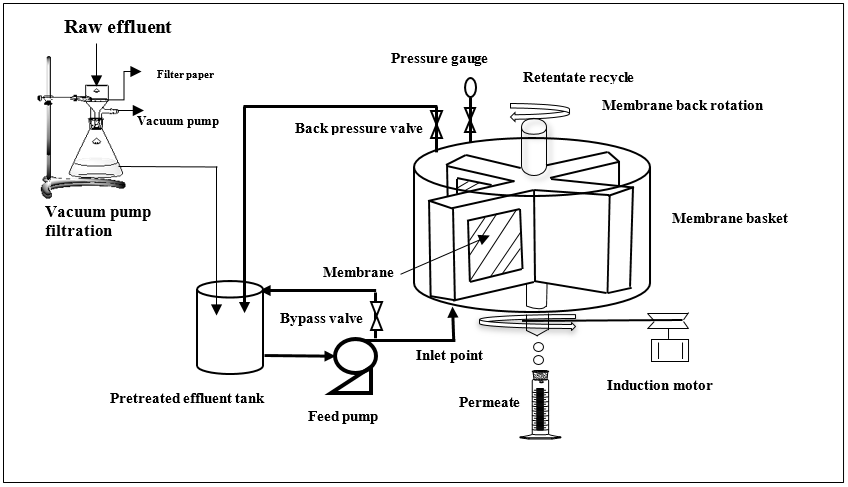
Figure: Treatment of Industrial effluents using spinning basket membrane ultrafiltration
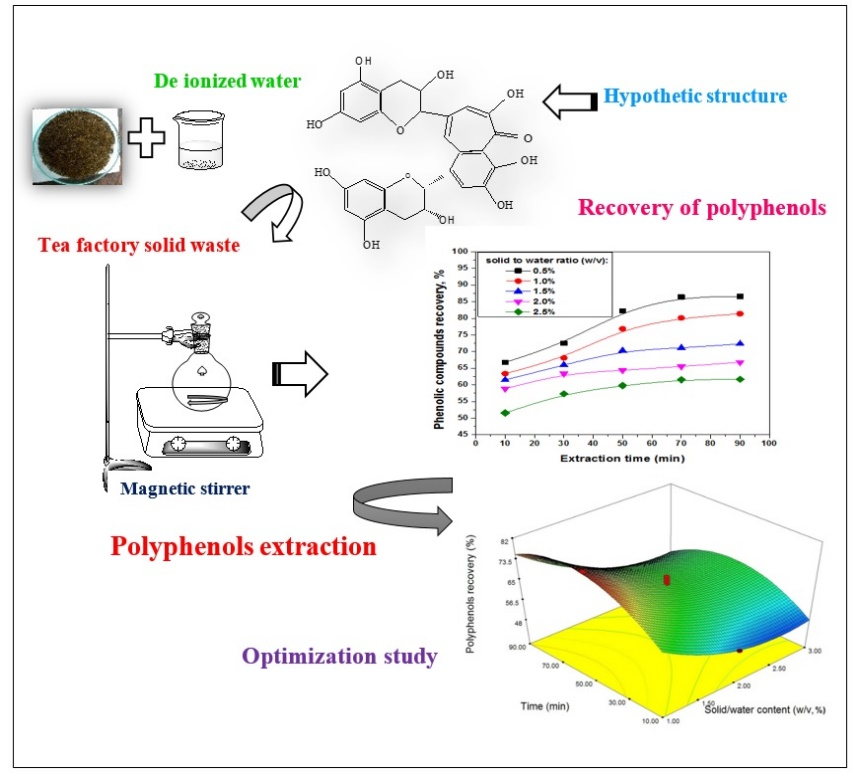
Figure: Utilization of tea factory solid wastes towards polyphenols separation
- A. Development of a Low-cost Catalytic Membrane Reactor for Sulfur Recovery
- The development of catalytic membrane and membrane reactor for the recovery of elemental sulfur using Claus reaction from H2S-laden gas processed as feed gas in the sulfur recovery unit (SRU) is deliberated. The problem associated with high manufacturing cost of the conventional catalytic membrane and membrane reactors encourage us to develop a novel scheme for the fabrication of catalytic membrane and membrane reactor. The purpose of fabricating catalytic membrane reactor is to minimize complications of the conventional sulfur recovery process using three catalytic bed reactors in the refineries. On the basis of the aforesaid problem statement, this entire study is divided into three segments and these are fabrication of low-cost tubular ceramic support membrane, synthesis of Mo-Co/γ-Al2O3 catalyst and fabrication of catalytic membrane by coating of the catalyst with a solid lubrication over the exterior surface of the ceramic support by using a simple coating technique. An experimental set up made of stainless steel is designed and fabricated to carry out a batch experiment at room temperature (28 ± 2ºC) to recover sulfur. This study claims that the fabricated reactor behaves like an ideal catalytic membrane reactor (CMR) by means of 87% yield and 80% conversion of reactant.
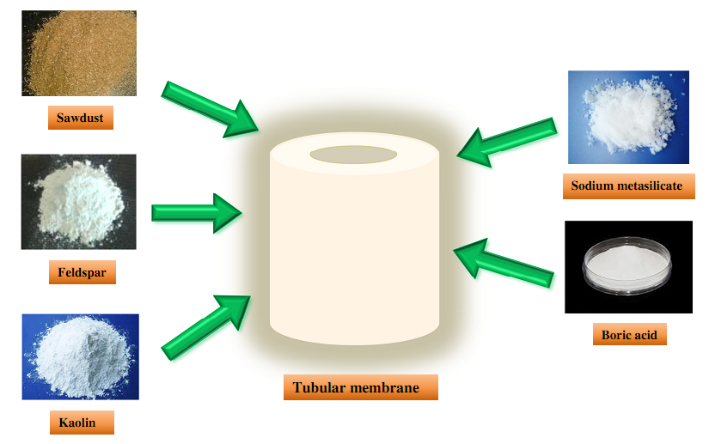
- Figure: Fabrication of tubular ceramic membrane
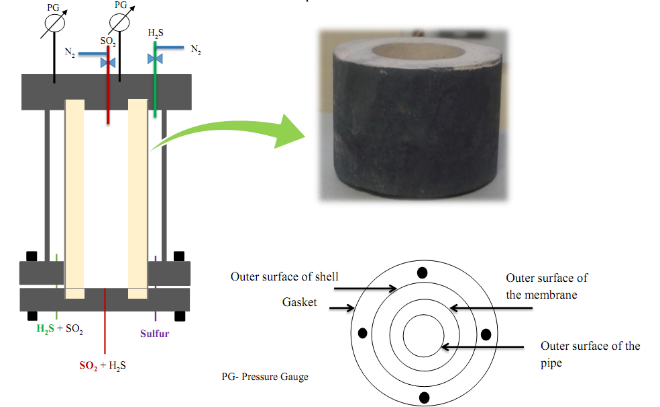
- Figure: Schematic of CMR
- Membrane separation is considered to be the most widely recognized advanced separation techniques in recent times. Over the years, remarkable researches have been carried out on the preparation, characterization and application of ceramic membranes which have led to the discovery of various low cost precursor based compositions. The use of saw dust as a pore former has been a major breakthrough while speaking about low cost precursors in addition to kaolin and feldspar as base material and sodium metasilicate and boric acid as binding agents. Mixture model design based composition optimization of membranes instigate the fabrication process which was followed by the application of optimized membranes in various process along with development of silver nanoparticle composite membranes. The membrane were intended to be applied for juice clarification and potable water production in terms of nutrient and bacteriostatic analysis.
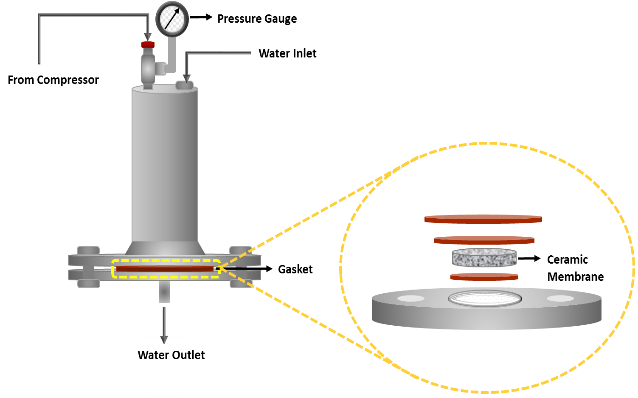
- Figure: Membrane permeation setup
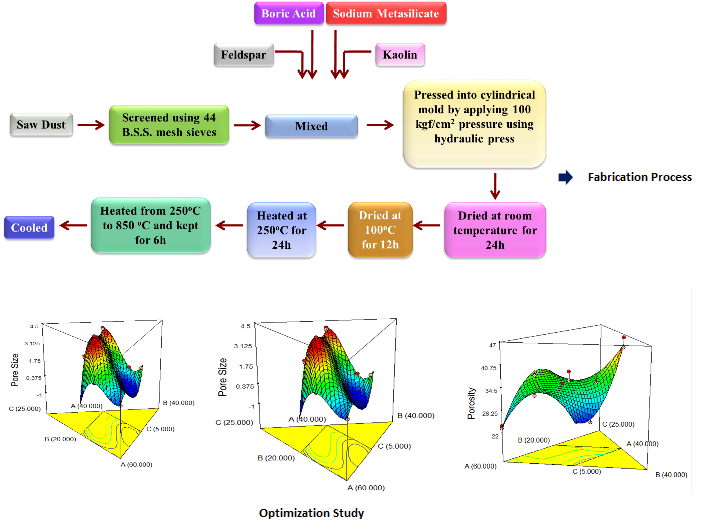
- Figure: Fabrication Process and Optimization Results
Biosorption process coupled with membrane filtration process was developed for heavy metal ion removal (Figure (a)). The hybrid process provides advantages of the high quantity of treated wastewater, high removal efficiency, better fouling control, low energy consumption and lower backwashing as compared to conventional treatment processes. Micellar enhanced ultrafiltration is another efficient wastewater treatment technique. MEUF can separate ions and small organic molecules in an aqueous medium which can only be separated using nanofiltration (NF) or reverse osmosis (RO) (Figure (b)). This process combines high selectivity of reverse osmosis process and high flux of ultrafiltration process. But the application of synthetic surfactant causes secondary pollution and add extra cost to the process. Saponin which is a natural biosurfactant derived from plants can be utilized in MEUF process effectively.
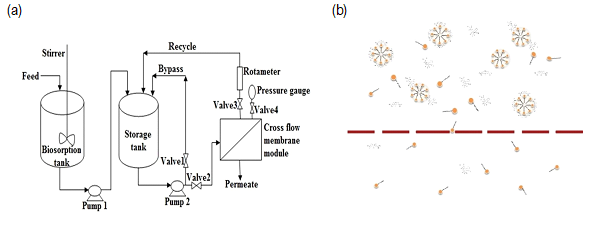
Figure: (a) Biosorption process followed by membrane filtration process. (b) Micelar enhanced ultrafiltration process using saponin biosurfactant.
Food Science & Technology
RA is a natural sweetener found in Stevia leaves. It is around 450 times sweeter than sucrose. The RA extract also contents many medicinal properties. Extraction of RA is performed by green solvent, water which shows considerable extraction efficiency. Water extraction reduces the cost since it eliminates the organic extraction of RA as well as eliminates number of unit operations. After successful extraction of RA, it is concentrated by membrane filtration followed by final moisture removing to make it in dry product.
Aloe Vera is a medicinal plant. It is mainly used for burn healing and skin aliment. Our main purpose is to make the Aloe Vera gel in completely dry form in such a way that it contents all of its medicinal properties. To achieve this goal, we are studying various drying processes and are comparing their physicochemical properties.
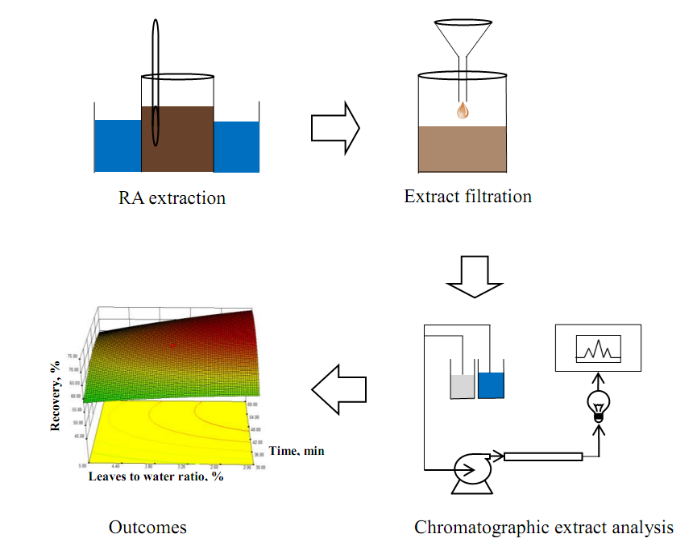
Figure: Extraction of RA
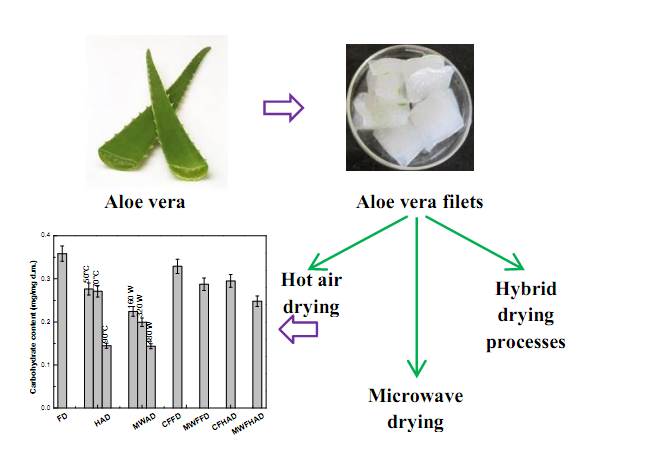
Figure: Drying of Aloe vera gel
Anthocyanins are one of the most commonly used water-soluble natural colorants, the vibrant colors that range from red to blue. Besides their vibrant colors, anthocyanins also have antioxidant and bioactive properties linked to certain health benefits such as anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects on human body. In our present study, we are extracting the anthocyanin and other various phenolic compounds from the purple rice bran. The anthocyanins are very much sensitive to heat, pH, light, and oxygen. Therefore, we are also investigating the degradation behavior of anthocyanin in various environmental condition. Furthermore, to protect the anthocyanin from the adverse effect of environment, we are microencapsulating the anthocyanin molecules in starch. At the end, we are applying the microencapsulated anthocyanin in a food system as a functional ingredient.

Figure: Microencapsulation of anthocyanin in starch
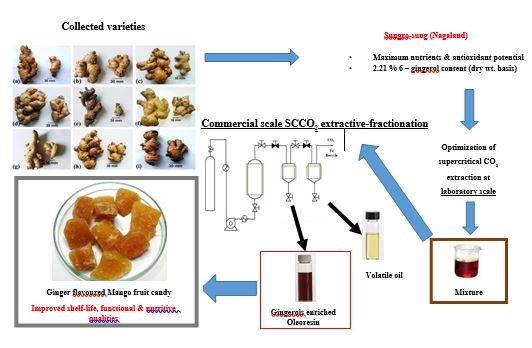
Antioxidants have a very vital role in our bodies and therefore have recently attracted huge attention as natural health products, dietary supplements and also as food stabilizers. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SCCO2) is a state-of-art technology which has emerged as an attractive extraction technique for food and pharmaceutical industries. Conventional solvent extraction methods are known to introduce traces of organic solvents in the extracts which greatly reduce their therapeutic value and may also lead to cancer inducing effects. SCCO2 has low critical temperature (31ºC), pressure (73.82 bar) and inert behavior, making it highly desirable for extraction of temperature sensitive compounds. The separation from extract is also simple and instantaneous leaving no residue hence producing “natural†extract. As opposed to liquid solvents, the solvating properties of SCCO2 can be altered by changing temperature and pressure which makes it possible to even separate/fractionate targeted compounds. All these properties make SCCO2 highly desirable for extraction and selectively separate a range of bioactive compounds, like, antioxidants, pigments, flavors, oleoresin, fatty acids, essential oil etc. from plant and animal sources.
We have successfully separated high quality oleoresin (non-volatile extractives of solvents) of ginger enriched with pungent principles like 6, 8 and 10-gingerols as major active ingredients, responsible for the characteristic hot taste. In addition, high quality volatile oil (steam volatile extract) has also been separated, which contributes for ginger’s unique aroma and contains α-zingiberene, β-sesquiphellandrene, ar-curcumene, β-bisabolene as major compounds. Both the extracts have a wide range of applications as flavorings in food and beverage industry as well as in fragrance industry. Apart from these, the oleoresin and volatile oil have also demonstrated to impart a wide range of therapeutic effects, such as, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, antipyretic, analgesic, gastro-protective action, etc. The process for SCCO2 extractive separation of both kinds of extracts has been optimized at laboratory conditions and has been successfully validated in commercial scale trails.
These extracts are produced in very high quality and purity and are, hence, used in commercial production of a wide range of pharmaceutical formulations. In addition, these compounds can be incorporated into solid/liquid food systems for improvement of their functional properties. The addition of compounds into a food matrix could protect them against deteriorating reactions and aid to modulate the release of these compounds being able to influence on their assimilation. We have successfully incorporated the infusion of gingerols rich oleoresin in development of fruit based products. The final products have demonstrated substantial improvement in overall qualities like sensory scores, total antioxidant activity and functional properties. In addition to the improved product quality, the incorporation of antioxidant rich extracts has demonstrated improvement in shelf life of the final products. Thus opening gates for innovative and healthy ‘safe’ and ‘natural’ food systems are manifested for growing need of health concerned population.
Sustainable Material for Corrosion Protection
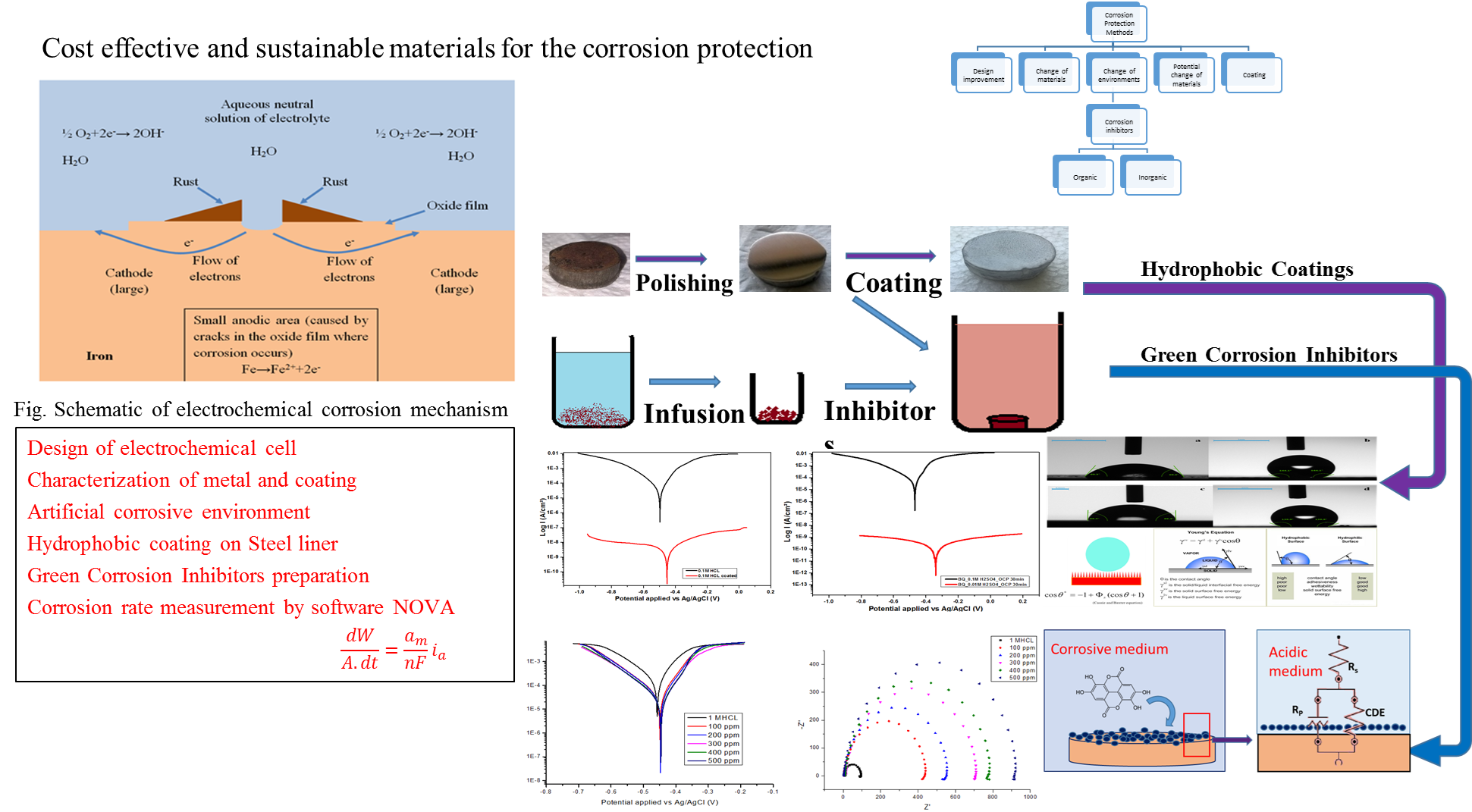
Corrosion is a galvanic process by which metals deteriorate through oxidation usually but not always to their oxides. For example, when exposed to air, iron rusts, silver tarnishes, and copper and brass acquire a bluish-green surface called a patina. Under ambient conditions, the oxidation of most metals is thermodynamically spontaneous. Corrosion has been a big threaten for every industrial and domestic area where materials are exposed to oxygen and water. There are various ways to protect the material from corrosion such as cathodic protection, anodic protection, coatings.
The prime objective of the current research is to find out the cost effective and sustainable materials for the corrosion protection. Our study is conducted for boiler quality (BQ) steel of ASTM (American society for testing and materials) grade A537 which are used in the power plants, like, The Kopili Hydro-Electric Project (KHEP) of North Eastern Electric Power Corporation Limited (NEEPCO) which is one of the pioneering Hydro-Electric Projects in the North Eastern Region (NER) of India. After characterizing the metal, corrosion rate is measured for the metal by performing potentiodynamic polarization test. It has been observed that as the acidic nature of the electrolyte or working solution increases corrosion rate and corrosion current density (Icorr) of metal in the respective solution also increases. Then the corrosion rate is measured for bare and coated metals. The coated BQ steel samples have shown a remarkable current density (Icorr) shift from 37.9 µA/cm2 to 0.03 µA /cm2 and from 59.87 µA/cm2 to 0.02 µA /cm2 with respect to Ag/AgCl for HCl and H2SO4 medium, respectively. The significant reduction in the corrosion current density (Icorr) in hydrophobic coated mild steel indicated the 99.99% corrosion resistance efficiency for both the chloride (Cl-) and sulphate (SO42-) medium.
Solid waste of tea factory which is used as green corrosion inhibitors are extracted using solid-liquid leaching process. This inhibitors of different concentrations from 100 ppm to 500 ppm are applied to corrosive solution of 1M HCl. At 500 ppm, the corrosion current reduction efficiency is found as 85%. After applying inhibitors, both the anodic reaction and cathodic reaction rates are depleted as anodic and cathodic current are depleted. This green corrosion inhibitors work as mixed type (anodic and cathodic) inhibitors.
Heavy metal remediation using Sprirulina pletensis, a blue-green micro algae
| 4.1. Spirulina Platensis for Decontamination of Chromium Laden Aqueous Effluent |
|
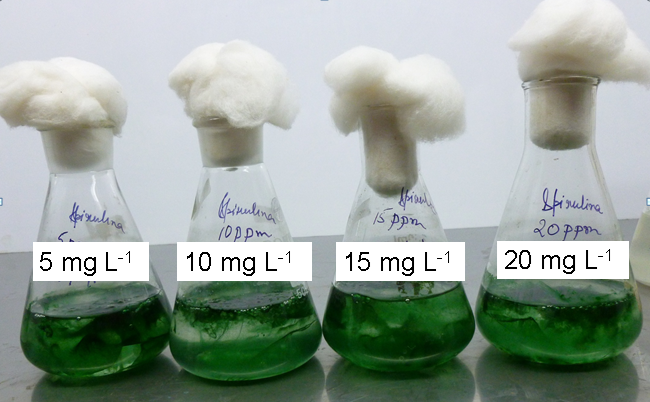
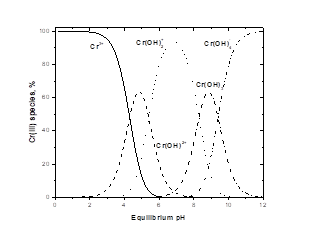
The applicability of Spirulina platensis, a blue-green microalgae for the removal of both Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution in batch reactor is explored. A second order kinetic model was developed for the reduction of Cr(VI) into Cr(III). The feasibility of precipitated chrome tanning effluent (PCTE) for the cultivation of Spirulina sp. was also investigated to utilize its Cl- resource. Figure: Spirulina cultivation in ZMC added with Cr(III) |